tensorflow Multi Gpus Tutorial
-
概述:
趁着,代码在跑的间隙来补一波这次做tensorflow 多GPU并行加速中遇到的一些坑。
参考资料:
tensorflow官网相关教程:https://www.tensorflow.org/tutorials/deep_cnn
github cifar-10相关代码:https://github.com/tensorflow/models/tree/master/tutorials/image/cifar10/
一遍不错总结坑的博客:https://blog.csdn.net/diligent_321/article/details/53187166
博客有介绍同步异步,很好理解:https://juejin.im/entry/58eb25fc61ff4b0061a88c0c基本思路:
gpu并行计算架构图:
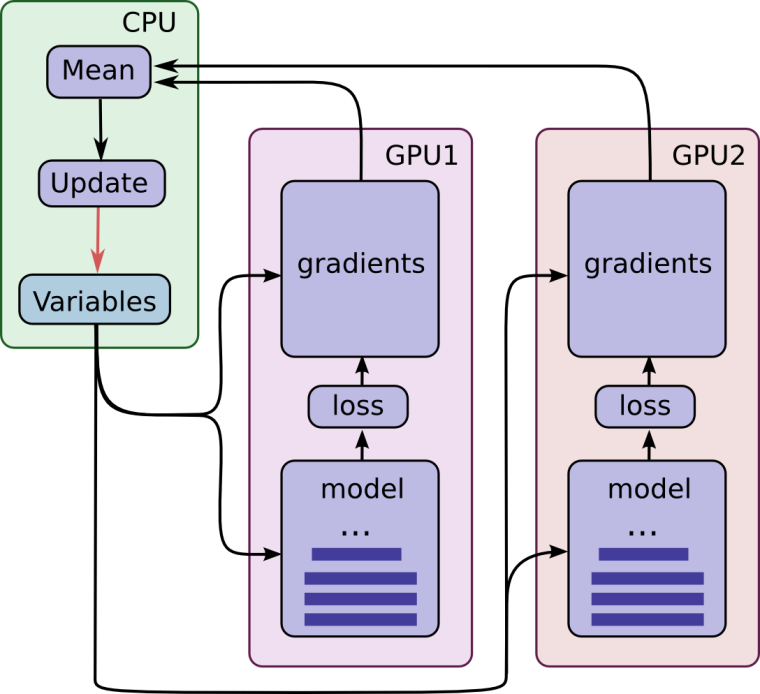
思路:- 每个gpu同时算Loss,然后一起更新参数
- 所有的变量需要有一个共享机制(variable_scope + get_variable)
- 同步方案(略慢,但是准确)、异步方案(有些网络结构对异步敏感)
- 尽量把所有的Op都放在gpu上
- 每个gpu喂的数据要不一样
数据共享与梯度平均
首先理解:tf.variable() 、 tf.variable_scope() 、tf.get_variable()
知乎大法:https://www.zhihu.com/question/54513728tf.variable() 和 tf.get_variable
tf.variable() 和 tf.get_variable是tensorflow中创建变量的两种方式,我们通过tf.device可以决定把这个变量放在哪个设备上,如果不给定,默认貌似在gpu第一块上。tf.get_variable可以获取之前定义过的变量,这个需要搭配tf.variable_scope(name,reuse=True)使用。
坑点:r1.7版本有个reuse=tf.AUTO_REUSE。但是r1.3并没有这个自动检测的功能,只能自己定义第一次定义变量后设置reuse=True。获取到之后,使用官网给的接口把grad求均值。#共享变量设置 with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()): for i in xrange(FLAGS.gpu_num): with tf.device('/gpu:%d' % i): #这里设置你自己的模型,获取一个loss即可 cur_loss = your_model() # 在第一次声明变量之后,将控制变量重用的参数设置为True。这样可以 # 让不同的GPU更新同一组参数。注意tf.name_scope函数并不会影响 # tf.get_ variable的命名空间。 tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables() # 使用当前GPU计算所有变量的梯度。 grads = train_opt.compute_gradients(cur_loss) tower_grads.append(grads) #求均值grads def average_gradients(tower_grads): """Calculate the average gradient for each shared variable across all towers. Note that this function provides a synchronization point across all towers. Args: tower_grads: List of lists of (gradient, variable) tuples. The outer list is over individual gradients. The inner list is over the gradient calculation for each tower. Returns: List of pairs of (gradient, variable) where the gradient has been averaged across all towers. """ average_grads = [] for grad_and_vars in zip(*tower_grads): # Note that each grad_and_vars looks like the following: # ((grad0_gpu0, var0_gpu0), ... , (grad0_gpuN, var0_gpuN)) grads = [] for g, _ in grad_and_vars: # Add 0 dimension to the gradients to represent the tower. expanded_g = tf.expand_dims(g, 0) # Append on a 'tower' dimension which we will average over below. grads.append(expanded_g) # Average over the 'tower' dimension. grad = tf.concat(axis=0, values=grads) grad = tf.reduce_mean(grad, 0) # Keep in mind that the Variables are redundant because they are shared # across towers. So .. we will just return the first tower's pointer to # the Variable. v = grad_and_vars[0][1] grad_and_var = (grad, v) average_grads.append(grad_and_var) return average_grads喂数据
其实本质上到这里,并行化就结束了,但是需要注意的是,对于不同的GPU我们需要给不同的数据,官网使用队列的方式,这里我任然使用feed_dict,这里额外注意,我们要拿到每个GPU上的每个输出变量,并在feed_dict时候字典对应,不然就GG了。下面给点示例代码:
#使用3个列表记录我的triple-net的输入变量。 query_input_list = [] doc_positive_input_list = [] doc_negative_input_list = [] with tf.variable_scope(tf.get_variable_scope()): for i in xrange(FLAGS.gpu_num): with tf.device('/gpu:%d' % i): input_result_ = input_layer(input_layer_num) query_input_list.append(input_result_[0]) doc_positive_input_list.append(input_result_[1]) doc_negative_input_list.append(input_result_[2]) cur_loss = get_loss(query_input_list[i],doc_positive_input_list[i],doc_negative_input_list[i]) tf.get_variable_scope().reuse_variables() grads = train_opt.compute_gradients(cur_loss) tower_grads.append(grads) #喂数据的时候按下面的方法对应变量去喂数据就好了。 def feed_dict_train_multi_gpu(): """ input: data_sets is a dict and the value type is numpy describe: to match the text classification the data_sets's content is the doc in df """ result_dict = {} result_dict[on_train]=True for i in range(FLAGS.gpu_num): query, doc_positive, doc_negative = pull_all() result_dict[query_input_list[i]] = query result_dict[doc_positive_input_list[i]] = doc_positive result_dict[doc_negative_input_list[i]] = doc_negative return result_dict###一些坑:
- 一定搞清楚每个变量的variable_scope
- 如果使用feed_dict,留下输入变量,feed的时候对应好
- 每个gpu要喂不同的数据
- 有些版本没有tf.AUTO_REUSE
- tf.concat()不同版本下变量顺序不同,copy代码请注意。
- 每个gpu同时算Loss,然后一起更新参数
-
前排膜凡宇聚聚
-

